Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region is a chronic degenerative-distrophic disease of the lumbar spine that affects the structure of the intervertebral discs and a number of located lumbar vertebrae.Affects people of age mainly work.It manifests itself in various symptoms, the main of which are the pain in the lower back and legs, limiting movements in the lower back.For diagnostics, research methods such as radiography, calculated tomography or magnetic resonance resonancet of the lumbar spine are used.In this article, you can more detail with the causes, symptoms and methods of diagnosing osteochondrosis of the spine.
Osteochondrosis is the result of body aging.These or other signs of this disease can be found in almost any person (!), Starting at 25 years.But here is the severity of these changes, the degree of their progress, the degree of clinical manifestations depends on many causes, largely on how a healthy lifestyle leads a specific person.Moderate physical activity, mandatory breakfast gymnastics, proper body pose when doing a number of work (garden, construction, banal cleaning of the house, etc.
According to statistics, spinal osteochondrosis in 80% of cases is the cause of back pain.
How does osteochondrosis develop?
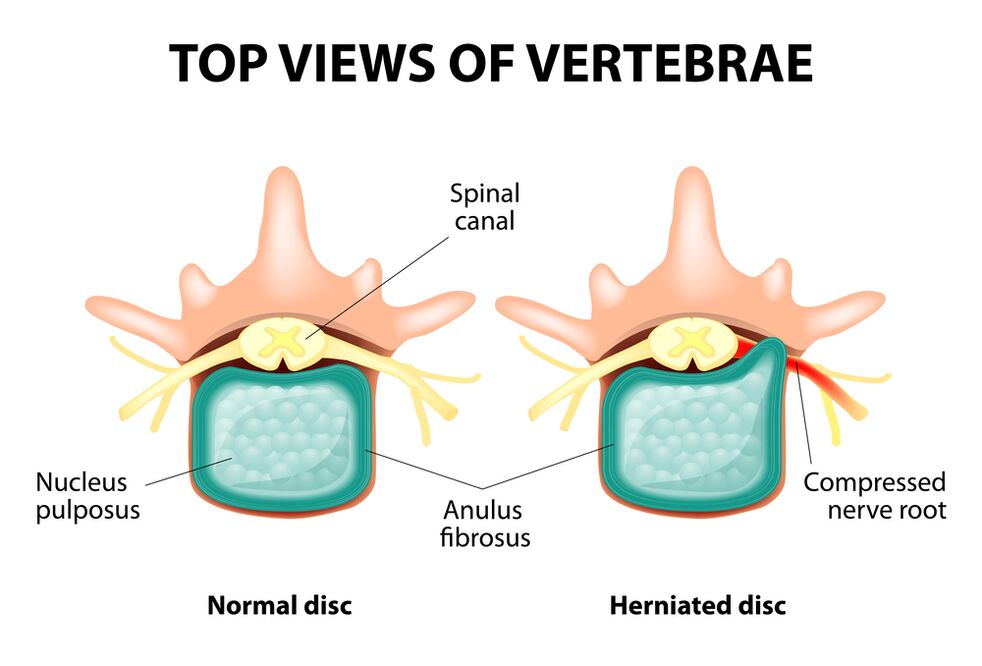
The entire spine consists of separate beads, between the bodies of which has intervertebral discs.That is to say, between the two beads is a disk.The disk consists of a gelatinous (pulpic) core and a fibrous ring.The nucleus contains a lot of water and provides depreciation and flexibility of the spine.The fibrous ring is located along the periphery of the jacket core, as if it holds it within itself.
With an extensive increased load at the essence of Jetty, it changes its physiological properties, loses water and dries, and eventually sequences: the disk is flattened, and vertebral bodies approach each other.Along with such processes, in the nucleus jacket, the fibrous ring loses its elasticity and, under the influence of mechanical loads, begins to extend.This is called extension.Then the cracks of the fibrous ring and a gelatinous core fall through the resulting gaps: a disc herniation appears.A plot of two adjacent vertebrae and a disk located between them, called vertebral segment, acquires excess mobility, thereby increasing the load on the nearby segments.The overload of neighboring segments causes a similar pathological process in them.These changes are called osteochondrosis.
To ensure the stability of the spine, bone growths form along the edges of the vertebral bodies, increasing the support area.This phenomenon is called spondylosis.Changes in the joints between the vertebrae are called spondylo arthrosis.Usually all three pathologies - osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyl arthrosis - walk close.
Reason
Why does osteochondrosis occur?So far, there are some theories of occurrence:
- Mechanical theory: Perhaps the main reason should be considered an increased regular load on the back.That is why osteochondrosis is an almost mandatory fate of motors, miners, builders and people of such professions.The emergence of lumbar region osteochondrosis is mainly associated with slopes and increasing severity, forced an unpleasant position of position;
- Another developing factor is incorrect attitude, sitting in the wrong position, which is especially important for mental employees;
- Sometimes the role is played by the inherited features of the spine structure and the food of its individual structures;
- Traumatic theory: any trauma to the spine (even more irrelevant) is able to begin a degenerative process;
- Disordishes hormonal metabolic disorders and endocrine diseases can adversely affect metabolism in spinal column tissue and contribute to the development of osteochondrosis;
- Age theory implies the natural dress of the discs in the process of life.
Rarely, only one of these theories can explain the appearance of osteochondrosis in each case.Most often at the same time, several factors are "to blame".
In the appearance of lumbar spine osteochondrosis, overweight plays an important role, as it is an overload for the spinal column itself.The higher the body mass index (the rate of being overweight), the more pronounced changes in the spine.Among other reasons that provoke the emergence of osteochondrosis, it can be emphasized:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- Imorly food (fast food, excessive, semi -finished products: all this leads to an imbalance of trace elements) and lack of fluid;
- abnormalities of the spine structure (for example, the presence of an additional lumbar vertebra);
- Continuous dressing of high behavior shoes;
- pregnancy (due to excess load on the lumbar spine);
- Sudden completion of training in people professionally involved in sports;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse: as factors that accelerate the aging process in the body.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of lumbar spine osteochondrosis is pain.The nature of the pain, the occurrence of the occurrence and the direction of the distribution depend on the receptors irritate, that is, how harsh changes in the disk and the surrounding tissue, there is extension or hernia, in which direction the extension was formed and so on.
Reflex and compression syndromes are distinguished by the osteochondrosis of the spine.
Reflex syndromes develop in cases where the fibrous ring ring receptors of the affected disk, ligaments and joint capsules placed close to irritate.They are reflexive because in addition to pain is accompanied by changes in muscular-tonic, vegetative-vascular or neurodyistrophic reflex, ie, irritation with reflexes is transmitted to other structures, causing symptoms mainly on the soft tissue.
Compression syndromes occur as a result of compression (compression) of the nerve roots, blood vessels or spinal cord formed by osteochondrosis from changes.

Spine reflex syndromes
Lumbago(Feeling): sudden acute pain in the lower back, which occurs with a difficult movement or at the time of physical tension (much less often - for no apparent reason).It is believed that the appearance of Lumbago is associated with the movement of a jacket nucleus within the fibrous ring, that is, it develops in the early stages of osteochondrosis.Often the pain is described as "feeling", the stake was stuck in the lower back. "Patients freeze in a position in which the pain caught them.The slightest movement causes an increase in pain (sneezing, coughing, an attempt to return to bed, to move your leg).If a person was in a prone position at the time of development of lumbago (which occurs most often), then he cannot be directed.A pronounced muscle tension in the lumbar spine occurs reflexively.Along the vertebrae in this area, there is a muscle roll, which is sometimes visible to the free eye without touch, and the muscle tension is so pronounced.Feeling painful for the patient.Such an increased muscle tone performs an immobilizing role, protecting the lumbar segment affected by pathological mobility, which can provoke a deterioration in the state.The natural curve of the spinal column at the lower back (lordosis) is flattened, perhaps bending (scoliosis) is possible due to muscle tension.
Lumbalgia- another lumbar level reflex syndrome.This term also implies the presence of pain in the lumbar region.But unlike Lumbago, the pain does not arise acutely, but gradually, within hours or even days.The pain is thick, with moderate intensity, intensifies during movements, in a sitting position or standing when moving from one position to another.A slight relief brings about the position of the stretch or back with a roller below the lower back, but the passive raising of the leg directed to this position causes increased pain in the lower back (Lassa symptoms).Lumbar spine palpation is painful, but reflex muscle tension is less pronounced than with lumbago, and sometimes missing at all.The movements in the lumbar spine are limited but possible.This means that the patient can bend and on the sides at a certain level (and then the pain intensifies).
Çatika- another variety of lumbar level reflex syndrome.This term means pain in the lower back, which gives the buttocks and in the foot (on the back surface).The pain is different, mostly painful, but can be periodically intensified by the type of "fireplace" in the foot.As with lumbalgia, it intensifies with every movement, walking, straining, decreases in the back.Lassa's symptom is usually positive.The palpation of the lumbar spine is painful, as well as pressing in a few points (for example, in the middle of the line that separates the buttocks from the thigh, between the back of the thigh, in the middle of the popliteal fossa).There is back muscle tension.The trends forward and on the sides are limited.

Lumbar back compression syndromes
The clinical feature depends on which structure is subject to compression.
Between the vertebrae in each intervertebral hole are the nerve roots (spinal nerves): left and right.If the pathological formations for lumbar spine osteochondrosis (mainly discs of the disc) squeeze the roots, then the radiculopathy develops, the symptoms of which vary for each root.Common to all radiculopathies of the lumbar region is the increase in pain during sneezing, coughing, movement at the lower back (especially the front slope), the presence of muscle tension at the lower back, limiting movements in the lumbar spine.The following types of lumbar spine radiculopathy are more common:
- Radiculopathy L1, L2, L3: The pain appears at the bottom of the back, gives the predicted thigh.In the same area, the emergence of paresthesia (a feeling of crawling of wells, numbness) is possible, superficial sensitivity is disturbed (an acute touch is usually not distinguished, the feeling of cold and hot) is lost.Knee reflex decreases, the weakness of the thigh quadrant is detected;
- Radiculopathy L4: The pain from the lower part gives the anterior part of the thigh, the inner surface of the knee joint and slightly lower along the inner surface of the lower leg.In the same areas, paresthesia and superficial sensitivity are felt (decreased).The weakness in the quadrilateral muscle of the thigh also develops, the knee reflex decreases;
- Radiculopathy L5: One of the frequent localizations.The pain gives the buttocks, along the outer edge of the thigh, along the anterior surface of the lower leg to the inner edge of the leg and thumb.Paresthesia feels here, superficial sensitivity is worried and a pain is given here when sneezing and coughing.In addition, there is a difficulty in stretching the thumb, as the muscle that performs this action has been inovated by the China L5.Sometimes it is difficult to stand on the heel with exposed heels;
- Radiculopathy S1 is often often found with osteochondrosis of the spine.The pain gives the buttocks, along the outer edge of the thigh, along the outer edge of the lower leg to the outer edge of the foot and the 5th finger, heel.These areas are characterized by a sense of paresthesia, a decrease in surface sensitivity.Achilles' reflex is reduced.With the damage of this back, the weakness of the lower leg muscles and the leg flexors develops, so staying and walking in the socks is difficult.
The simultaneous development of radiculopathy of some roots is possible, this is particularly characteristic of L5, S1.It happens that a hernia squeeze some roots.
If the disk tuft climbs back, then it can squeeze the spine.This is only possible when the hernia is located at the upper point of reference, as there are no spinal cord beads under the lumbar vertebra II (spinal cord roots undergo compression, and horse tail syndrome develops).
If the vessels of the lumbar region undergo squeezing, which perform the blood flow to the spinal cord, then in the case of an acute circulatory disorder, a spinal stroke develops, and with prolonged compression - myelopathy.Myelopathy is manifested by the bilateral weakness of the leg muscles, starting from the foot and gradually progressing.Foot sensitivity is disturbed, Achilles' reflex is lost, and later knee.It is possible to appear urination disorders (frequent, "indispensable" demand, which requires immediate pleasure, urinary incontinence).
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of lumbar spine osteochondrosis is based on clinical data and data of additional research methods.The main role belongs to such methods as:
- Lumbar spine radiography;
- calculated tomography of the lumbar spine;
- The magnetic resonance tomography of the lumbar spine.
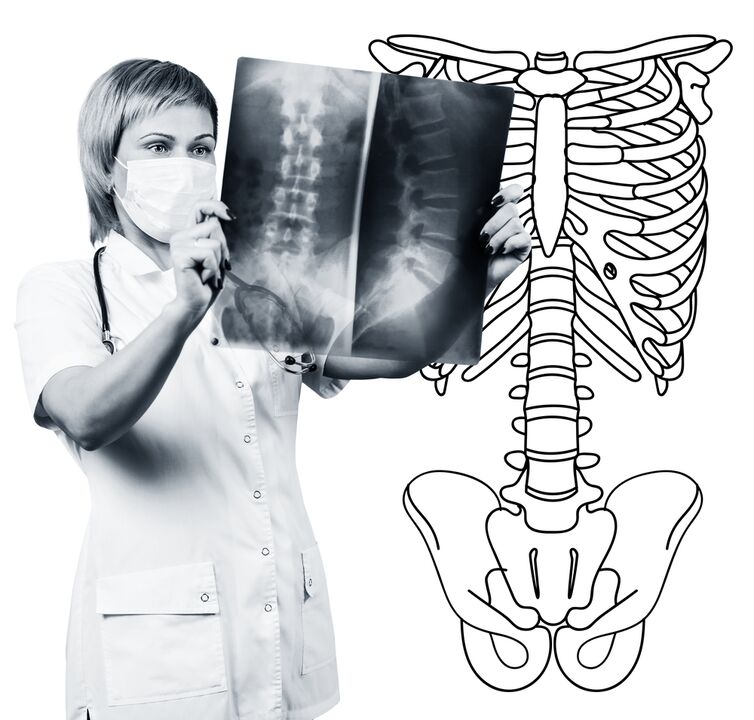
Lumbar spine radiography is necessarily performed in 2 mutually perpendicular and lateral projections.Such photographs allow you to see the shape, contours and structure of vertebral bodies, height and shape of intervertebral discs, spinal abnormalities and natural curves.To display intervertebral joints and intervertebral holes, radiograms are produced in oblique projections.To identify the pathological mobility of individual lumbar segments (which is a sign of osteochondrosis), radiography is performed under functional test conditions, that is, in the bending and extension of the spine.Normally, you can clearly see the difference in the height of the intervertebral discs in the front or rear sections in accordance with the direction of the body's propensity, with osteochondrosis due to the functional block of one of the segments, the height of the disc does not change either when bending or extending.With pathological mobility, the shift of vertebrae forward or backward is determined.The main signs of osteochondrosis X -Ray include narrowing of the intervertebral cleft, pathological mobility and the displacement of vertebral bodies, deposition of salts in the disk tissue (calcification), the formation of regional growth of vertebral bodies, compacting vertebrates in the limit (s).Lumbar spine radiography is a research routine, which gradually loses its importance in the background of active implementation of new and more informative research methods (CT and MRI).Lumbar department radiography is used today as a diagnostic method of review.
CT of the lumbar spine is also performed using X -ray radiation, but the radial load on the body is much less than with X -Ray.The study is performed lying on the table of a special device - a computer tomographer, is absolutely painless.The resulting photos are processed using a computer and allow you to see more structures significantly more than with spinal radiography.
MRI is a method in which electromagnetic radiation is used to create images.The study is also performed in the position of stretch on the table, which calls to the tomography room.MRI is harmless and painless.
CT or MRI of the lumbar spine allow you to see all spine structures, carefully examine the intervertebral discs (and the fibrous jacket) and the intervertebral holes, the contents of the spinal canal.Even a slight extension of the intervertebral disc will not pass unnoticed.These methods (especially MRI) allow you to determine the direction of the disc herniation if there is, the degree of compression of the nerve roots, the spinal cord.Thus, these research methods are much more informative in the diagnosis of lumbar back osteochondrosis than radiography.Moreover, they allow you to diagnose not only osteochondrosis but also other diseases (tumors, spinal cord disorders, abscesses, congenital defects of the spinal cord structure and spinal cord), which are important during differential diagnosis of the causes of the spine.
Lumbar spine osteochondrosis is a disease that most commonly causes back pain.It is, in fact, the destruction of the intervertebral discs.Due to the osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, a person often loses the ability to work, as, in addition to pain, the disease can lead to a violation of spine mobility, inability to sit, to stay and walk.Symptoms of this disease are non -specific and require additional research methods to accurately confirm the diagnosis.Most informative and secure of modern methods of diagnosing osteochondrosis is the spine MRI.


























